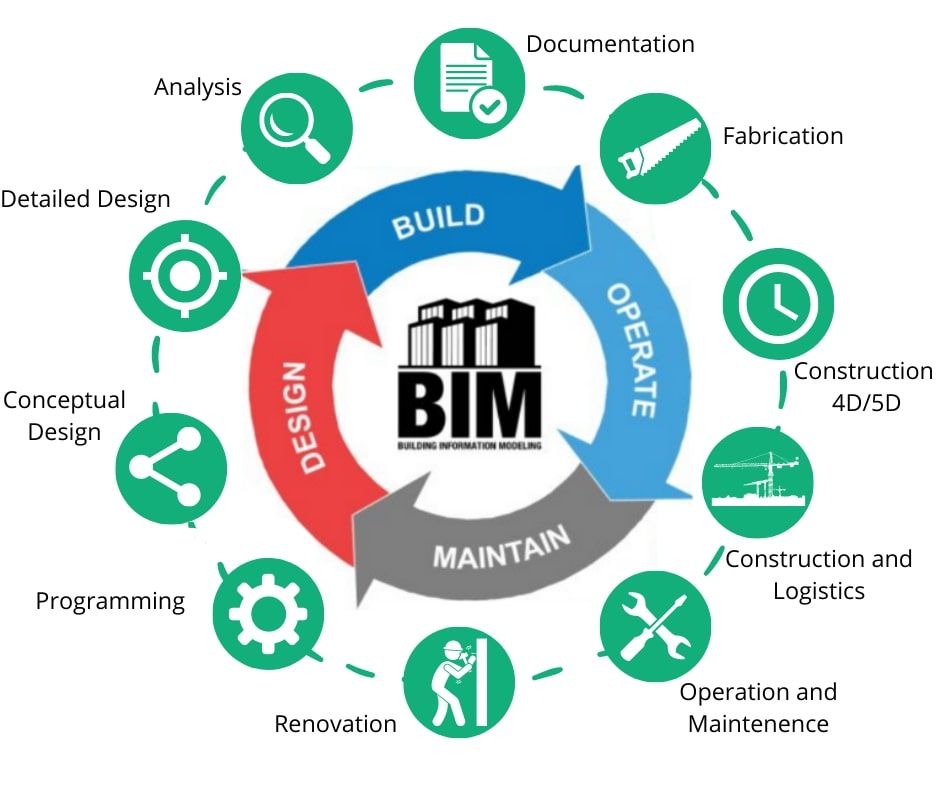
Building Information Modeling (BIM) has revolutionized the architecture, engineering, and construction (AEC) industry by providing a collaborative platform for designing, constructing, and maintaining buildings. However, BIM interoperability issues can hinder the smooth flow of data across multiple software applications and platforms used in the AEC industry. To overcome these challenges, BIM interoperability tools have been introduced to facilitate seamless integration and exchange of data between different software applications used in the AEC industry. This article will explore the importance of BIM interoperability tools and how they enhance collaboration among stakeholders in the AEC industry.
Understanding BIM Interoperability
BIM interoperability refers to the ability of different software applications and platforms to exchange data efficiently without losing or corrupting information. It involves integrating multiple software applications into a single platform that can be used by all stakeholders involved in a construction project. For instance, architects may use Autodesk Revit for designing building models while structural engineers use Tekla Structures for analyzing and designing steel structures. Contractors may use Navisworks for clash detection and coordination while facility managers use ArchiFM for managing building assets.
However, these software applications may not be compatible with each other due to differences in file formats, data structure, and software versioning. Therefore, BIM interoperability tools are necessary to facilitate the exchange of data between different software applications.
Benefits of BIM Interoperability Tools
1. Enhance Collaboration
The main benefit of BIM interoperability tools is that they enhance collaboration among different stakeholders involved in a construction project. By allowing multiple software applications to integrate seamlessly, stakeholders can work on a single platform without worrying about compatibility issues. This enhances communication and reduces errors since everyone is working with the same data set.
2. Improve Productivity
BIM interoperability tools also improve productivity by reducing the time spent on data conversion and manual data entry. Instead of wasting time converting files to different formats, stakeholders can focus on more important tasks such as design, analysis, and construction. This improves efficiency and reduces project timelines.
3. Reduce Costs
BIM interoperability tools also reduce costs by eliminating the need for multiple software licenses and reducing errors caused by manual data entry. By using a single platform, stakeholders can save money on software licenses and training costs. Additionally, BIM interoperability tools reduce errors caused by manual data entry which can lead to rework and additional costs.
Types of BIM Interoperability Tools
1. File Format Converters
File format converters are used to convert files from one format to another without losing or corrupting information. For instance, IFC (Industry Foundation Classes) is a neutral file format used in BIM to exchange data between different software applications. Therefore, file format converters such as Autodesk Revit IFC Exporter, Tekla Structures IFC Exporter, and Solibri Model Checker are necessary for converting files from proprietary formats to IFC format.
2. Middleware Applications
Middleware applications act as a bridge between different software applications by allowing them to communicate with each other through a common interface. Examples of middleware applications include bimserver.org, which acts as a central server for exchanging data between different BIM software applications; Flux.io, which allows users to share BIM data across multiple platforms; and Speckle.works, which facilitates real-time collaboration among stakeholders using different software applications.
3. API Integrations
API (Application Programming Interface) integrations allow different software applications to interact with each other through predefined functions or protocols. For instance, Autodesk Forge API allows users to access Autodesk BIM 360 services through a common programming language such as Python or Java. Similarly, Rhino.Inside.Revit API allows users to run Rhino Grasshopper scripts inside Autodesk Revit.
Conclusion
BIM interoperability tools have become essential for enhancing collaboration and productivity among stakeholders involved in a construction project. By allowing multiple software applications to integrate seamlessly, BIM interoperability tools reduce errors and improve efficiency, ultimately reducing costs and project timelines. File format converters, middleware applications, and API integrations are some of the most common types of BIM interoperability tools used in the AEC industry.
References:
1. https://www.autodesk.com/solutions/bim-interoperability
2. https://www.bimobject.com/en-us/blog/why-bim-interoperability-is-important
3. https://www.nibs.org/page/bsa_bim_interop
Hyperlinks:
1. Autodesk Revit – https://www.autodesk.com/products/revit/overview
2. Tekla Structures – https://www.tekla.com/products/tekla-structures
3. Navisworks – https://www.autodesk.com/products/navisworks/overview
4. ArchiFM – http://archifm.net/
5. IFC (Industry Foundation Classes) – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Industry_Foundation_Classes
6. bimserver.org – https://bimserver.org/
7. Flux.io – https://flux.io/
8. Speckle.works – https://speckle.works/
9. Autodesk Forge API – https://forge.autodesk.com/
10. Rhino.Inside.Revit API – https://www.rhino3d.com/inside/revit/beta/